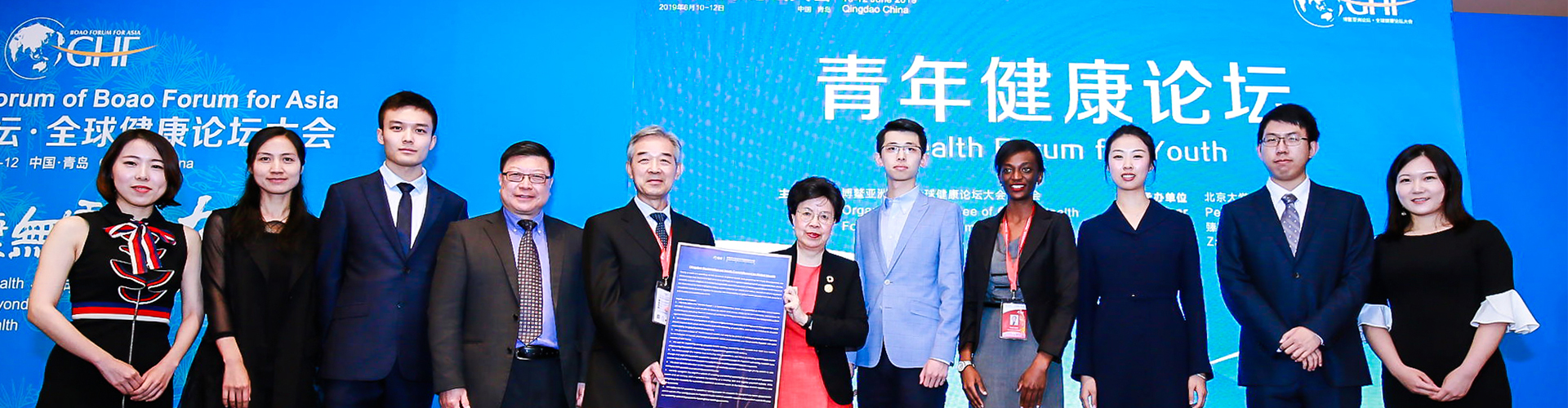
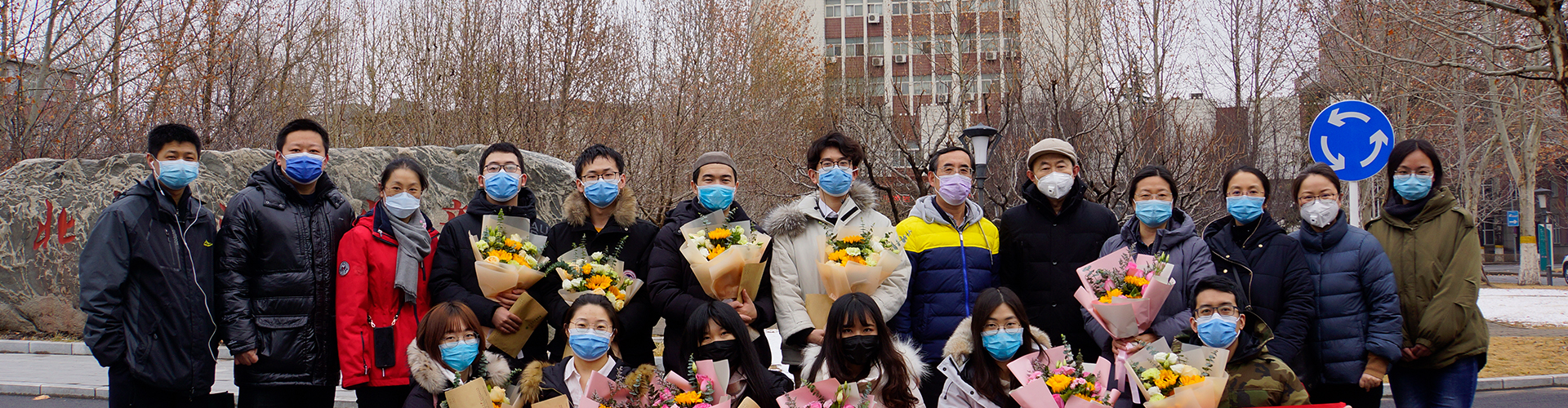
团队队伍
生命早期营养:母子营养与健康队列研究与平台建设;生命早期营养与喂养状况对婴幼儿生长发育影响追踪研究等;一碳单位代谢与生命早期母子健康;出生缺陷相关易感基因关联研究和全基因组连锁分析。
员工营养:个体(营养素养)及食物环境对儿童饮食行为发展及营养状况的影响;探索以学校为基础的营养教育与营养服务综合干预策略等。
1. 母子营养与健康队列研究与平台建设(湖南澳优食品与营养研究院专项项目)
2. 生命早期营养与喂养状况对婴幼儿生长发育影响追踪研究(横向合作)
3. 儿童饮食行为及其相关因素调查(中国社会科学院财经战略研究院)
4. 非综合征性唇腭裂易感基因定位研究(国家自然科学基金面上项目,教育部新世纪优秀人才支持计划)
5. 人群营养素养测量工具的建立及评价(联合国儿童基金会项目)
6. 以学校为基础的学龄儿童营养教育课程体系建设及评价(中国疾病预防控制中心)
7. 小员工集体用餐行为系统模型建立及其干预模式探讨(中国红十字基金会)
1. 社区食物环境与儿童肥胖的定性循证研究[J]. 中国学校卫生, 2021, 42(11): 1613-1615.
2. Dietary patterns of Chinese puerperal women and their association with postpartum weight retention: Results from the mother-infant cohort study[J]. Matern Child Nutr. 2021, 17(1): e13061.
3. Development and validation of a food and nutrition literacy questionnaire for Chinese school-age children[J]. PLoS One. 2021, 16(1): e0244197.
4. Maternal Postpartum Feeding Anxiety was associated with Infant Feeding Practices: Results from the Mother-Infant Cohort Study of China[J]. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth. 2020, 20(1):780.
5. Adjusting DBI-2016 to dietary balance index for Chinese maternal women and assessing the association between maternal dietary quality and postpartum weight retention: A longitudinal study[J]. PLoS One. 2020,15(8): e0237225.
6. 中国 0~24月龄城市婴幼儿母乳喂养状况及相关因素分析[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2020, 26(10): 77-81.
7. 学龄儿童家庭食物环境评价工具构建及信效度分析[J]. 中国食物与营养, 2020, 26(6): 74-79.
8. Effect of Smo SiRNA-mediated Hedgehog Signaling Pathway Inhibition on Palatal Fusion[J]. Biomed Environ Sci, 2016; 29(8): 594-598.
9. Association between interferon regulatory factor 6 gene polymorphisms and nonsyndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in a Chinese population. The Cleft Palate-Craniofacial Journal, 2013,50(5):570-576.
10. Genome-wide and interaction linkage scan for non-syndromic cleft lip with or without cleft palate in two multiplex families in Shenyang, China. Biomedical and environmental sciences, 2010, 23: 363-370.